Fingerprinting SSH Identification Strings
For HTTP, logging and fingerprinting browser user agents is standard practice. Many anti-automation tricks use the user agent and compare it to other browser artifacts, for example, supported JavaScript APIs, to detect bots. SSH offers an "identification string" with a format mandated by RFC 4253.
The RFC mandates this format:
SSH-protoversion-softwareversion SP comments CR LF
For example:
SSH-2.0-billsSSH_3.6.3q3<CR><LF>
With SSH 2.0 being the only SSH version that should be in use currently (I know... IoT... ), all identification strings should start with SSH-2.0-. The server and the client will send an identification string. But let's first focus on clients.
Why should you care about SSH identification strings: Just like user agents, looking for anomalies can be useful to detect compromise, or outdated clients and servers that may be present in your network. The identification string, as well as the ciphers offered, are exchanged in the clear. Tools like Zeek are nicely able to extract this data for analysis.
Let's go over some of the top different ssh clients that I see in our honeypot data.
I looked through some of our honeypot data to identify common patterns in identification strings. As a quick breakdown before diving into details, the main implementations I saw:
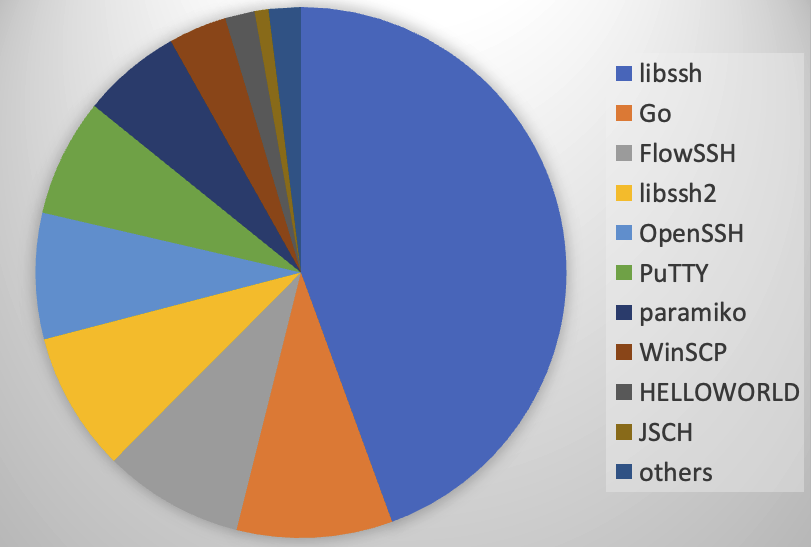
libssh
One of the most common libraries to implement ssh clients is libssh. Currently, versions 0.9 and 0.10 are supported, with 0.10.6 and 0.9.8 being the most recent versions. There is also a very similar libssh2, which appears to be updated more frequently. The most recent libssh2 version is 1.11.0.
Here are the top 10 "libssh" identification strings from our honeypots:
4331094 SSH-2.0-libssh-0.6.3
4270423 SSH-2.0-libssh_0.9.6
1137866 SSH-2.0-libssh2_1.10.0
425204 SSH-2.0-libssh2_1.4.3
99634 SSH-2.0-libssh2_1.9.0
83101 SSH-2.0-libssh-0.6.0
82085 SSH-2.0-libssh_0.4.8
81603 SSH-2.0-libssh_0.5.5
81380 SSH-2.0-libssh_0.11
80949 SSH-2.0-libssh-0.3.4
Note that many of the common versions are very much out of date. This could be an artifact of scanning tools using either hard-coded identification strings or them using outdated libraries. Remember that they may use the library present on the random (outdated) compromised IoT device they infected.
The most common libssh version in my home network is 0.9.3.
OpenSSH
Another very common SSH implementation is OpenSSH. In particular, on Linux systems, it is the preferred SSH implementation.
Top 10 identification strings for OpenSSH:
339860 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.4
213486 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.2p1 Ubuntu-4ubuntu0.5
162726 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.3
81907 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.2
81697 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_4.3
81595 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_6.2
81575 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_3.9p1
81467 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.9
81440 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_6.0p
81332 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_6.1
Ubuntu 22.04 uses SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.9p1 Ubuntu-3ubuntu0.5 as its identification string. The second one is close and could be a slightly older Ubuntu version. Current Macs use SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.4.
Putty
Using a lot of Windows systems? You may have users using Putty. Of course, bots and scanning tools will use this identification strings to "blend in":
250595 SSH-2.0-PuTTY
163900 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.63
162709 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.62
81663 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.61
81477 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Snapshot_2010_02_20
81420 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.62.1
81391 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_KiTTY
81349 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.58
81267 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.67
81189 SSH-2.0-PuTTY_Release_0.59
Go
Go is a language that has made a name for itself for creating efficient, multi threated network servers and clients. So no surprise that it is used for scanning tools. My random sample only had one specific identification string:
SSH-2.0-Go
paramiko
Of course Python users want to play with ssh as well. Paramiko is a Python module implementing ssh.
163066 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.8.1
82258 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.16.0
81923 SSH-2.0-paramiko_2.0.0
81786 SSH-2.0-paramiko_2.1.2
81674 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.15.1
81568 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.10.1
81532 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.7.7.1
81490 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.16.1
81410 SSH-2.0-paramiko_2.1.1
81234 SSH-2.0-paramiko_1.17.1
Other odd once:
FlowSsh (SSH-2.0-8.35 FlowSsh)
Another ssh library. See https://www.bitvise.com/flowssh
HELLOWORLD (SSH-2.0-HELLOWORLD)
probably not good. Not sure which exact tool this is.
ZGrab 9 (SSH-2.0-ZGrab ZGrab SSH Survey and SSH-2.0-zgrab2 opt-out available at http://195.37.190.89/)
part of the ZMap scanner. See https://zmap.io/
check_ssh (SSH-2.0-check_ssh_2.3.1)
the "check_ssh" plugin used by network monitoring tools like Nagios and Icinga.
---
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
| Application Security: Securing Web Apps, APIs, and Microservices | Orlando | Mar 29th - Apr 3rd 2026 |


Comments