Encrypted Client Hello: Ready for Prime Time?
Last week, two related RFCs were published:
RFC 9848: Bootstrapping TLS Encrypted ClientHello with DNS Service Bindings
RFC 9849: TLS Encrypted Client Hello
These TLS extensions have been discussed quite a bit already, and Cloudflare, one of the early implementers and proponents, has been in use for a while.
Amidst an increased concern about threats to privacy from government and commercial interests, the "encrypt everything " movement has been on the rise for a while. The community made several improvements to TLS, such as TLS 1.3, the QUIC protocol, the deprecation of OCSP, and encrypted DNS modes, to better protect the privacy of network traffic.
There was one data leak left: For a client to establish a TLS connection, it needs to send a "TLS Client Hello" message. This message contains several sensitive items, most notably the hostname of the site the client attempts to connect to ("Server Name Indication"). One of the early proposals was just to encrypt the Server Name Indication extension. But this does not solve the entire problem, allowing for fingerprinting and other attacks. The same basic principles proposed for encrypting the server name extension can also be applied to encrypt most of the client hello message, resulting in a more complete solution.
One of the basic problems is exchanging key material. The client hello message is the first message sent during the TLS handshake. There is no opportunity for the server and client to negotiate an encryption key, and doing so would require a second handshake. Instead, encrypted client hellos leverage the HTTPS DNS record. The HTTPS record is already used to negotiate HTTP3/QUIC. It is now also used to transmit the keys required for Encrypted Client Hello (ECH).
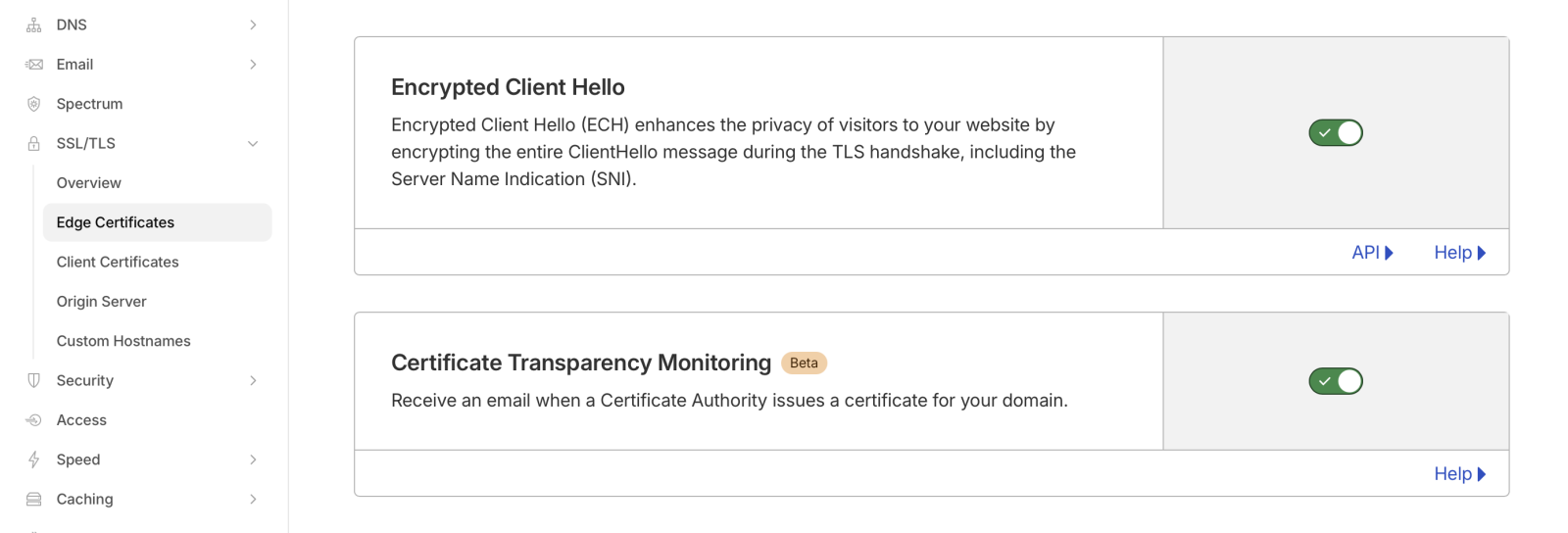
Enabling ECH is trivial if you are using Cloudflare. Just "flip the switch" in Cloudflare's edge certificate settings. However, I do not believe this is available on the free plan.
To test if a domain supports ECH, use a tool like "dig" to retrieve the HTTP record:
# dig -t HTTPS dshield.org +short
1 . alpn="h2" ipv4hint=104.26.2.15,104.26.3.15,172.67.70.195 ech=AEX+DQBBawAgACBRVO1kCb5b2znHUOTe+L42PHgEjBSNt4LD/qDNxffkAgAEAAEAAQASY2xvdWRmbGFyZS1lY2guY29tAAA= ipv6hint=2606:4700:20::681a:20f,2606:4700:20::681a:30f,2606:4700:20::ac43:46c3
Note the "ech=" part. Without ECH support, you may still see an HTTPS record, but it will not contain the "ech=" part. The base64 encoded string following "ech=" contains the public encryption key used to encrypt the client hello. A good test is cloudflare-ech.com, which will show whether your browser is using ECH. You can also use that domain to check if you are seeing the HTTPS record.
When using "dig", make sure you are using a version that supports HTTPS records. Older versions may not, and even the latest version of dig for macOS does not support HTTPS records. You will see a warning (which, as I found out, is easily missed), and you may still get "A" record responses:
% dig -t HTTPS dshield.org +short
;; Warning, ignoring invalid type HTTPS
For all the network traffic analysts grinding their teeth: You could block HTTPS records. This will also prevent QUIC from being used, which may be in your favor. But whether this is appropriate or not for your network is a question you must answer based on your business.
--
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|


Comments